For HR professionals working in the UK, Gender Pay Gap reporting will have most likely been a hot topic issue for the past few years. With the Gender Pay Gap Information regulations that came into effect in April 2017, employers with more than 250 relevant employees are required to publish a snapshot of their employee data detailing the difference in average pay for male and female employees by 4 April 2018.
There are a number of questions to answer when developing your approach to Gender Pay Gap reporting:
- Do I need to submit a Gender Pay Gap report?
- Which employees should be included in my report?
- What data do I need to report on?
- How should the values be calculated?
The regulations are quite clear that all organisations with more than 250 relevant employees as of the snapshot date must submit an annual Gender Pay Gap report. The first question that needs to be answered is: what is a relevant employee? In the broadest sense, this is anyone who has a contract of employment with your organisation. This will usually not include agency workers or directors, but HR Professionals should investigate these further, as there are some exceptions to these rules.
Once you know which employees to include in your headcount, count them up and if there are more than 250 heads, you will be required to produce a Gender Pay Gap Report. It is important to note that when calculating the headcount, you must not use FTEs (Full Time Equivalents); each employee counts as one head regardless of whether they work 10 or 40 hours per week.
The snapshot date for organisations in the UK is 5 April each year for the private and voluntary sector, and 31 March for the public sector.
Which employees should be included in my report?
The employees that need to be included in your report are known as Full-Pay Relevant Employees, that is, any Relevant Employees who are on full pay as of the snapshot date. So any employees who are on reduced pay for any reason – such as maternity or sick leave – must be included in your headcount, but not be included in your Gender Pay Gap calculations.
What data do I need to report on?
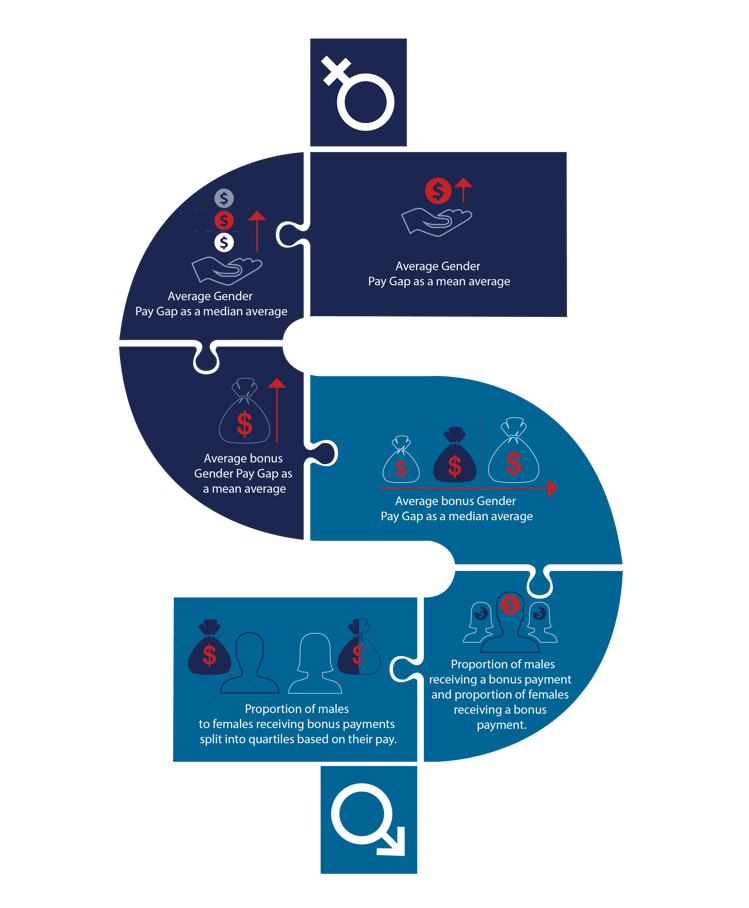
The two key pieces of data for Gender Pay Gap reporting are hourly rate and bonus payments, and you need to report on six metrics:
• Average Gender Pay Gap as a mean average
• Average Gender Pay Gap as a median average
• Average bonus Gender Pay Gap as a mean average
• Average bonus Gender Pay Gap as a median average
• Proportion of males receiving a bonus payment and proportion females receiving a bonus payment.
• Proportion of males to females receiving bonus payments split into quartiles based on their pay.
When determining someone’s pay, the key things to know are:
- All payments for the pay period in which the snapshot date falls should be considered
- Overtime payments should not be included
- Bonus payments are included, but should be pro-rated from the bonus payment period to the relevant pay period
- Allowances such as shift premiums, first aid allowances and car allowances are included
- The value of a company car is not included
- For organisations that have salary sacrifice, pay should be calculated after the salary sacrifice deductions.
| Weekly | Total pay for the period divided by the weekly hours |
| Fortnightly | Total pay for the period divided by 2 then divided by the weekly hours |
| 4 Weeks | Total pay for the period divided by 4 then divided by the weekly hours |
| Monthly | Total pay for the period divided by 30.44, multiplied by 7 then divided by the weekly hours. |
For the average bonus gap calculations, all bonuses paid in the relevant bonus period should be included, and should include payment such as performance bonuses, commission and profit share. So if your organisation has an annual bonus scheme, all bonus payments from the snapshot date and the previous 12 months need to be included.
How should the values be calculated?
Once all of the relevant employees, relevant full-pay employees, normal pay values and bonus pay values have been determined, the six different metrics can be calculated. The method for calculating these metrics is very specific. This is the approach that should be taken for each one:
The percentage gap between male and female pay and bonuses is defined as:
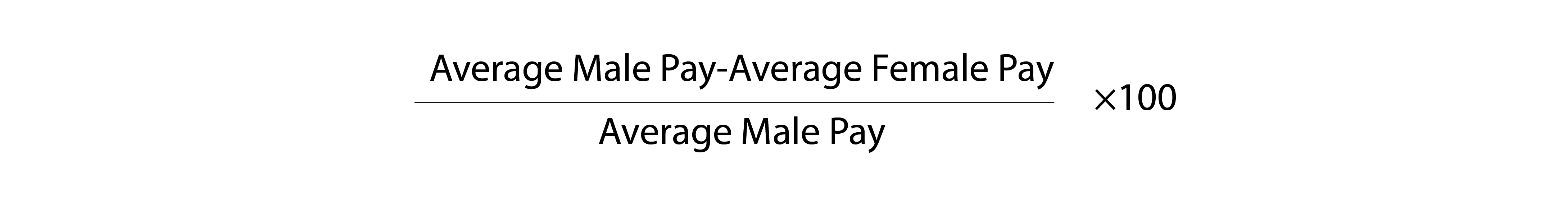
This formula can be used for the first four metrics when determining the mean and median gap for ordinary pay and bonus payments.
To calculate these metrics, we first need to determine the following values to plug into the formula:
• Average Gender Pay Gap as a mean average
- Mean average pay for males
- Mean average pay for females
- Median average pay for males
- Median average pay for females
- Mean average bonus payment for males
- Mean average bonus payment for females
- Median average bonus payment for males
- Median average bonus payment for females
When calculating the proportion of male and female employees that received a bonus, it is a simple case of dividing the number of male employees who received a bonus by the number of male relevant employees and the number of female employees who received a bonus by the number of female relevant employees and multiplying the values by 100.

and

Finally, you are required to calculate the percentage split of male to female employees that by quartiles based on their ordinary pay. This statement is a bit hard to get your head around, but the process is quite simple:
- Rank all full-pay relevant employees in order of their hourly pay
- Split the list of employees at the median value
- Calculate the median value of the two new lists and split those two lists into two further lists, creating a total four lists of roughly equal length, these are the four quartiles
- Count the number of male and female employees in each quartile
- For each quartile, calculate the percentage of male and female employees (For example, if there are 6 males and 4 females in a quartile, the split would be 60% to 40%).
There is no legal obligation to include any data other than the six metrics outlined above. However, organisations are encouraged to provide additional data that may help to provide a narrative to the metrics, or demonstrate actions being taken to address a Gender Pay Gap in your organisation. As some food for thought, additional metrics that you may want to consider including in your Gender Pay Gap Report are:
- Age profile by gender
- Length of Service by gender
- Salary Sacrifice participation by gender
- Flexible working usage by gender
- Promotions in year by gender
As outlined in a recent BBC article, at around six weeks to the submission deadline only 1047 firms had submitted their reports, leaving another 8000 to go. Organisations are struggling to find and compile their data, causing additional stress on already stretched Human Resources teams. The bad news for these teams is that this process is here to stay, and Gender Pay Gap data gathering and reporting exercises need to be cemented into their processes. With the first submission being treated as a proof-of-concept by many organisations, using massive, complex spreadsheets to compile their figures, organisations should be giving serious thought to how they can use technology to ease the burden and make Gender Pay Gap reporting a sustainable process.
Gethin Jones
An experienced Services Consultant in the Europe region, Gethin Jones specialises in products and services developed around SAP HCM. Gethin joined EPI-USE Labs a few years ago, having previously spent ten years in Human Resources. This background gives him invaluable insight into SAP HCM, and the benefits Query Manager can bring to an organisation's reporting strategy.
Insights from SAP experts and industry leaders
Subscribe todayTags:
HR |
HCM |
HCM Reporting |
Query Manager |
SAP |
reporting |
sap query hr |
SAP HCM reporting |
Gender Pay Gap